Vision 2.0: Vision Language Models & Agents at the Edge
Vision Language Models (VLMs) are revolutionizing computer vision, ushering in a new era—Vision 2.0. These models bring unprecedented flexibility and intelligence to visual systems:
- Generic: Adaptable across a wide range of tasks
- Low-code/No-code: programmable with natural language prompts.
- Autonomous: Trigger actions in agent-based systems
- Powerful: Understand context without fine-tuning
The real potential of VLMs is unlocked when they’re deployed at the edge. By processing data locally, VLMs at the edge eliminate network bottlenecks and ensure data never leaves the device—ideal for sensitive or time-critical tasks. Advancements in edge GPUs and model optimization techniques now make it feasible to run powerful VLMs outside the data center.
VLMs don’t just see—they understand. Their outputs can be chained into action-triggering pipelines, enabling autonomous and semi-autonomous agentic systems which combine perception and action—VLMs interpret the world and trigger next steps automatically, like sending alerts or controlling hardware.
Visum AI: Turnkey Edge Deployment for Vision 2.0
Visum AI offers full-stack, edge-deployable vision 2.0 solutions tailored to customer-specific requirements.
Achieving consistent, high-quality performance from VLMs requires careful consideration of factors like:
- Model architecture selection
- Model size (parameter count)
- Latency and memory optimizations (e.g., pruning, distillation, quantization)
- Domain-specific fine-tuning
- System enhancements like Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) and Cache-Augmented Generation (CAG)
- Agentic capabilities such as tool use
Visum AI’s platform addresses all these challenges—no machine learning expertise required. Our turnkey solution dramatically simplifies deployment, allowing customers to focus on what matters: results. To start a conversation or schedule a demo, contact us at contact@visum.ai or book a demo.
Real-World Applications
Visum AI’s Vision-Language Model (VLM) solutions are already demonstrating strong performance across a variety of industrial and operational scenarios. Below are some of the most impactful and common use cases where VLMs bring measurable value.
Visual Quality Inspection
Detecting surface anomalies, misalignments, or manufacturing defects in real-time. One specific scenario is automated detection of packaging defects in production environments.
The VLM accurately identifies and localizes a tear in the product packaging, even under suboptimal lighting. This level of precision enables early defect detection, reduces manual inspection overhead, and helps prevent costly downstream errors—improving both product quality and throughput.

Model Evaluation: Choosing the Right Model for Defect Detection
Model selection is not one-size-fits-all. Visum AI helps customers navigate this trade-off, delivering optimized pipelines that balance accuracy, latency, and compute requirements to fit each deployment environment.
Here, we evaluated two models — a small model quantized to 4 bit, and a large model quantized to 8 bit precision — to illustrate how model selection impacts performance in real-world defect detection scenarios. The results highlight the importance of aligning model complexity with operational needs.
Detecting a Crack in a Ceramic Cup
The small model failed to detect the crack, while the large model successfully identified and localized the damage. For subtle or critical defects, higher-capacity models offer the reliability required for quality-sensitive workflows.

Identifying Damage to a Shipping Box
The small model detected the damage, but lacked descriptive detail. The large model provided a detailed, accurate assessment of the damage. Larger models not only detect issues more consistently but also deliver richer contextual understanding—crucial for automation, reporting, and downstream decision-making.

Intrusion Detection on Production Lines
Identify foreign objects on automated packaging lines to prevent contamination or system damage. The small model successfully detects the foreign object. The large model detects the object and provides contextual details about its type and position. While both models flag the anomaly, the richer output from the larger model supports automated decision-making (e.g., stopping the line, categorizing severity) without human intervention. This improves line safety and minimizes downtime.

Workplace Safety Surveillance
Detecting PPE violations, unsafe behaviors, and hazardous conditions proactively. Detecting hazardous objects in shared workspaces prevents accidents and ensures compliance. Small model correctly identifies the knife. The larger model also identifies the knife, and correctly concluding that its hazardous. In this case, both models meet the detection threshold. The smaller models may be suitable for static, lower-risk environments—while the larger models can be reserved for dynamic or mission-critical zones where nuance and context matter more.

Smart Operator Support System
Providing real-time visual context and guidance to human operators in complex machine environments. Small model misses one part in the count; fails to recognize identical components. The larger model accurately counts parts and identifies closely matching items. Overall, VLMs reduce reliance on human checks by delivering higher precision in visually repetitive tasks. This enables faster operations, lowers error rates, and supports workforce augmentation in high-mix, low-volume environments.

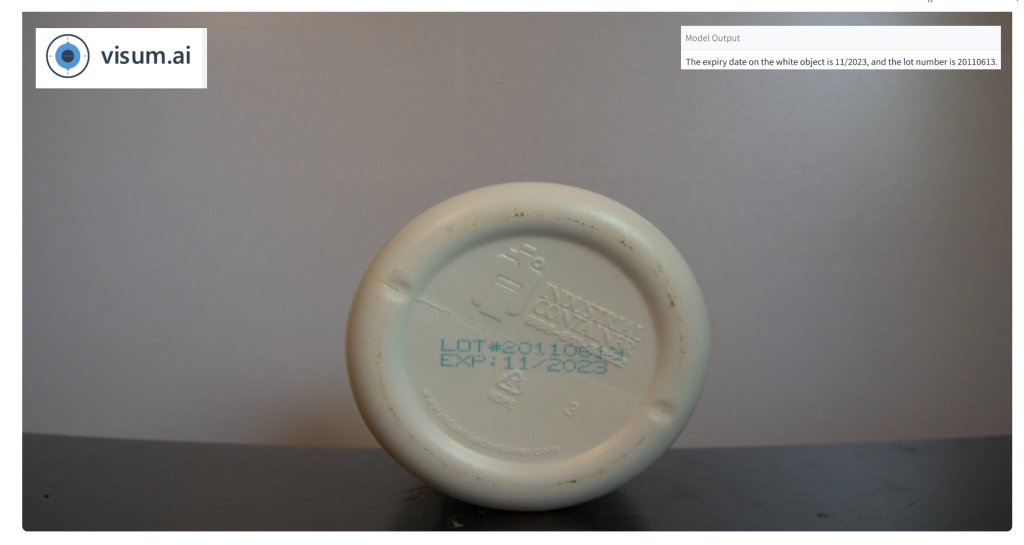
Industrial Text Recognition
Extracting structured data such as lot numbers, expiration dates, and serial codes from labels in real-world conditions.
The VLM reliably reads essential data such as lot numbers and expiration dates, even in less-than-ideal conditions (e.g., poor lighting, curved surfaces). This capability reduces dependency on traditional OCR tuning, minimizes errors in downstream logistics and compliance processes, and accelerates time-to-insight across production and supply chain operations.